It was the strongest GDP growth since Q2 2021 mainly boosted by domestic demand as the economy re-emerged from COVID curbs. With finance minister Suzuki saying the government will coordinate closely with the BOJ market attention is turning to what the bank could decide at its Sept.
Deepening The Culture Of Fear The Criminalization Of Peaceful Expression In Malaysia Hrw
The main reasons for policy intervention are.

. Japans government said it was ready to take action if rapid one-sided moves in the currency market continue signalling their alarm over the yens fall to a fresh 24-year low. The education system is. To correct for market failure.
The public sector also called the state sector is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. What are the main reasons for government intervention. Quotas are used in.
Malaysias economy advanced by 89 yoy in Q2 of 2022 accelerating sharply from a 50 growth in Q1 and easily beating market consensus of a 67 rise. Adding more sand to beaches is among the soft measures that the government employs to protect Malaysias shorelines from coastal erosion. In the meantime human intervention is still necessary in the form of temporary barriers built to protect young seedlings and provide a calm environment for mangroves to take root.
The main legislation governing education is the Education Act 1996. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military law enforcement infrastructure public transit public education along with health care and those working for the government itself such as elected officials. A quota is a government-imposed trade restriction that limits the number or monetary value of goods that can be imported or exported during a particular time period.
Household consumption picked up strongly 183 vs 55 in Q1 as did fixed investment. In 5 June 2008 gasoline prices had increased by 40 from RM192 per liter to RM270 per liter. Education in Malaysia is overseen by the Ministry of Education Kementerian PendidikanAlthough education is the responsibility of the Federal Government each state and federal territory has an Education Department to co-ordinate educational matters in its territory.
Malaysias government have spends US14 billion in term of subsidizing of gasoline diesel and gas each year. 21-22 policy meeting which will.

Impacts Of Covid 19 On Firms In Malaysia Results From The 3rd Round Of Covid 19 Business Pulse Survey
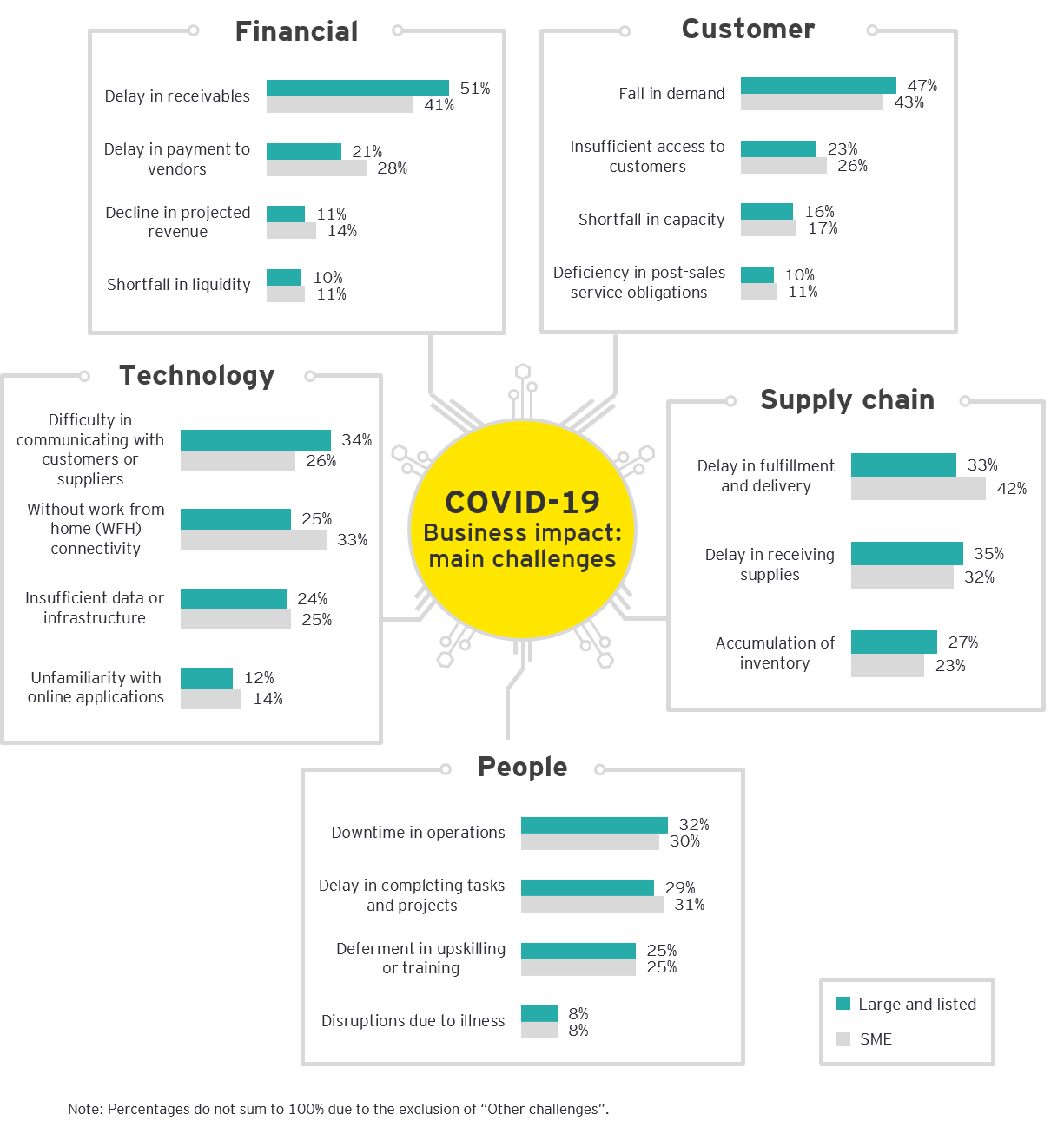
Covid 19 Impact On Malaysian Businesses Ey Malaysia

Mygov Obtaining Facilities Welfare Health Care

The Epidemiology Of Covid 19 In Malaysia The Lancet Regional Health Western Pacific

1 3 Government Intervention Ppt Download
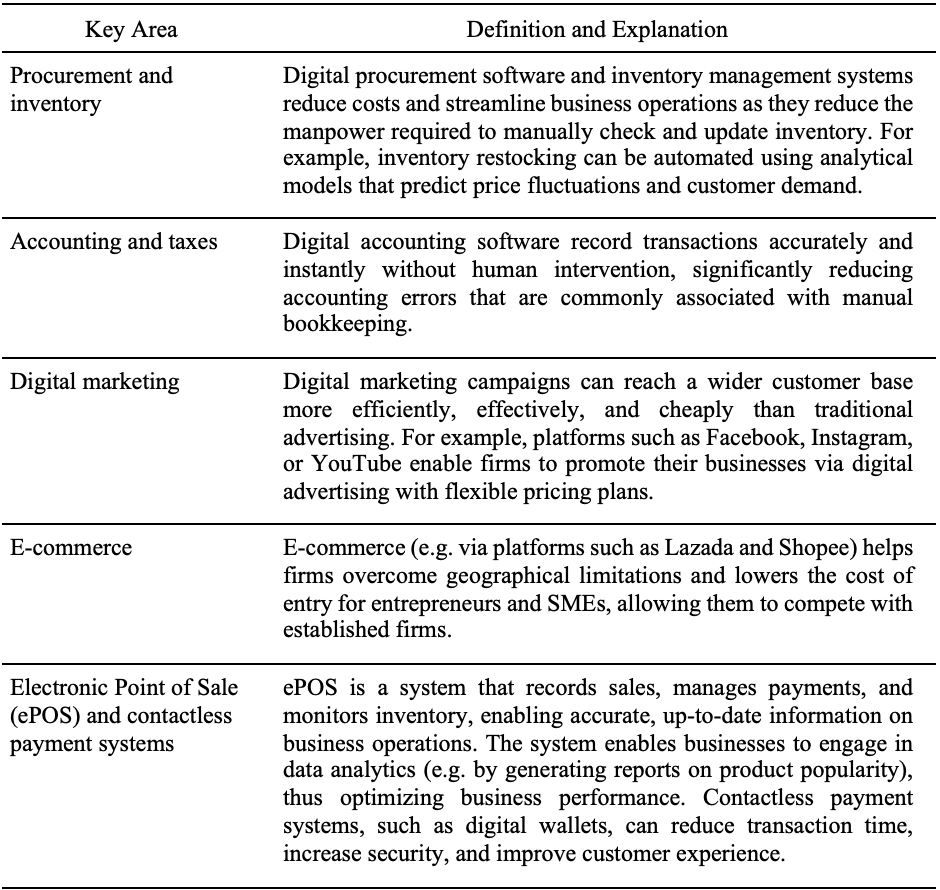
The Impact Of Covid 19 On Sme Digitalisation In Malaysia Lse Southeast Asia Blog
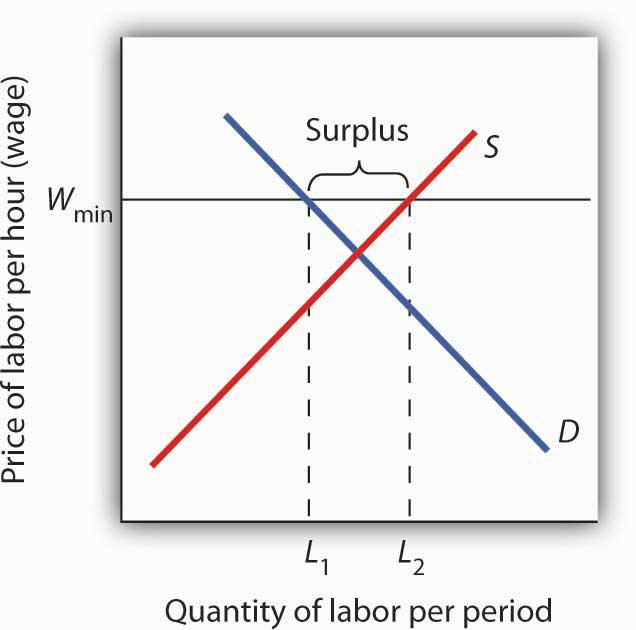
4 2 Government Intervention In Market Prices Price Floors And Price Ceilings Principles Of Economics
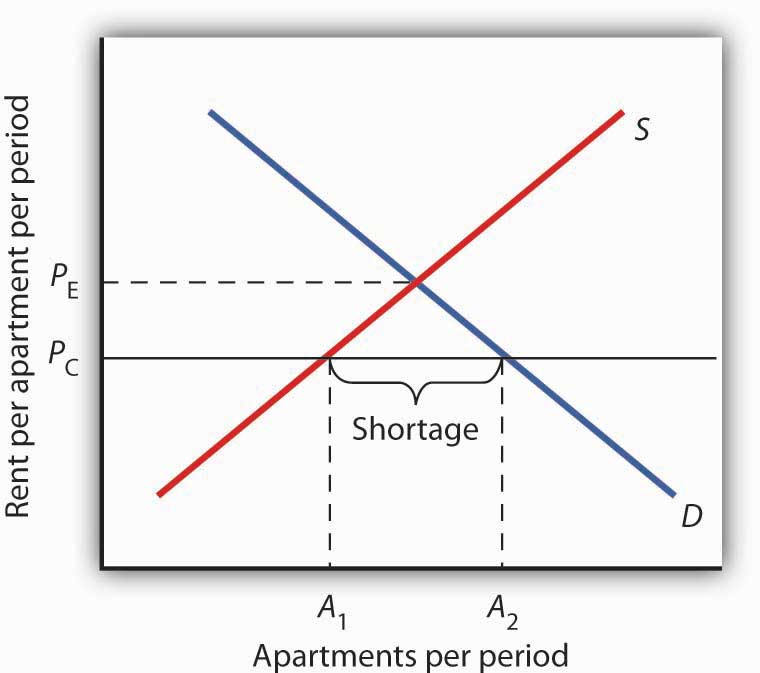
4 2 Government Intervention In Market Prices Price Floors And Price Ceilings Principles Of Economics
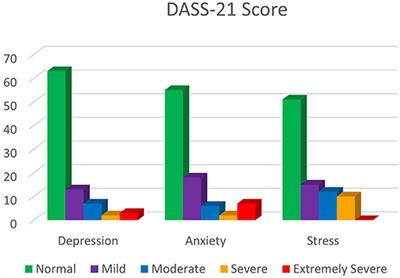
Frontiers Promoting Mental Health During The Covid 19 Pandemic A Hybrid Innovative Approach In Malaysia
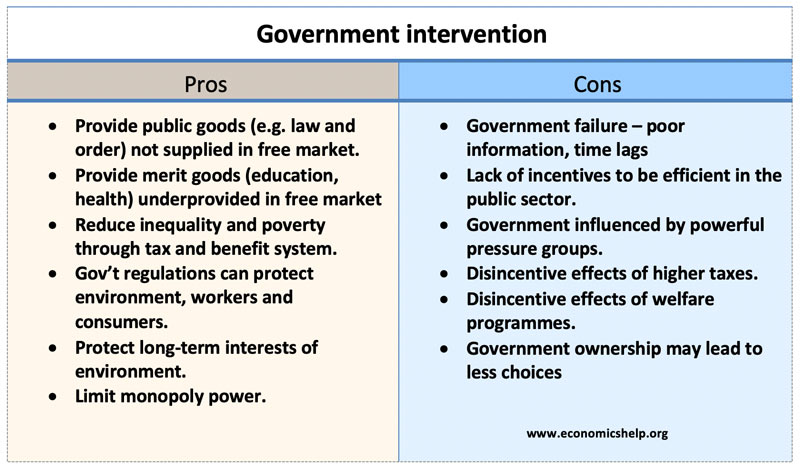
Pros And Cons Of Government Intervention Economics Help

Monarchy Reshaped As Malaysia S King Looks To End Political Turmoil Reuters
Malaysia To See More Rate Hikes Before End 2022

Malaysia S Political Polarization Race Religion And Reform Political Polarization In South And Southeast Asia Old Divisions New Dangers Carnegie Endowment For International Peace

Frontiers Enhancing Socio Economic Development Spurred Through Sti Policy Framework Into The Nucleus Off Mainstream Society In Malaysia

